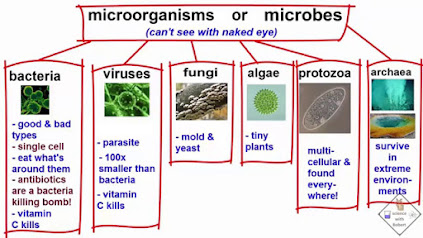
ARTIFICIAL SYSTEM OF CLASSIFICATION

The system of classification in which only one or two morphological characters are used for the grouping of organisms is called the artificial system of classification. Aristotle divided animals into two categories i.e. Enaima (with red blood) and Anaima (without red blood). Sometimes habit and habitat of animals are used to group them. Aristotle also grouped animals into Aquatic (living in water like fishes, whales, etc.), Terrestrial (living on the ground like reptiles, cattle, humans, etc.), and Arial (those animals who can fly like bats, birds, etc.) Aristotle Img: Google.com This is one of the earliest systems of classifications that used only the gross superficial morphological characters such as habit, color, number and shape of leaves, etc. Drawbacks of an artificial system of classification: It does not study homology (similarity of the structure, physiology, or development of different species of organisms) but is mostly based on convergence (The organisms evolve bodily...